Free Shipping on orders of $100 or more!

Education
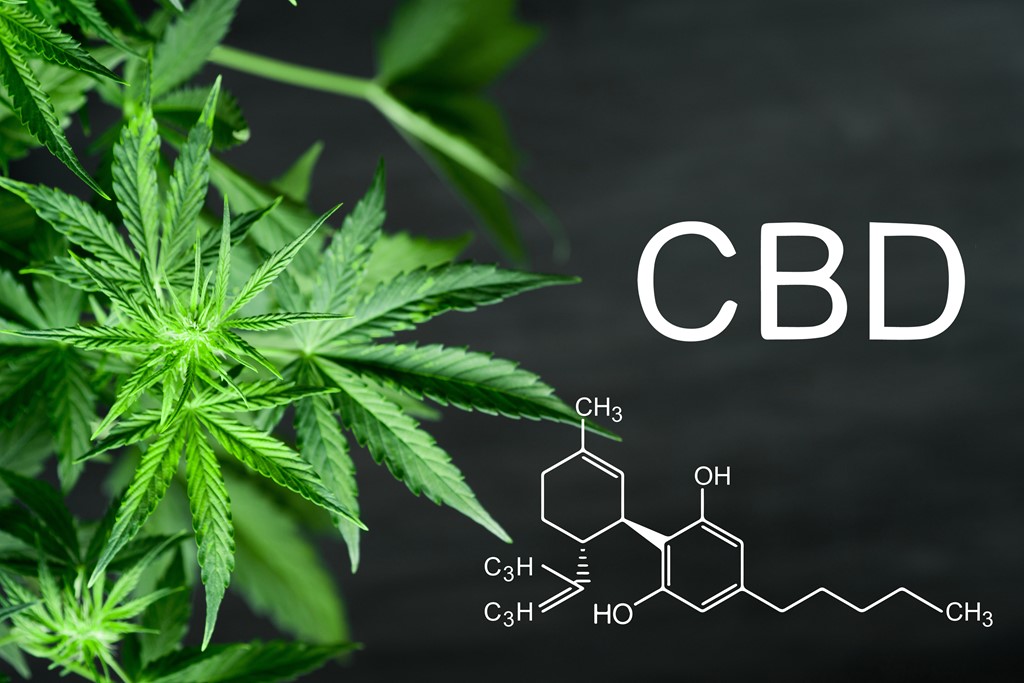

What is CBD?
What is exactly the CBD Oil? Where does it come from? How is it made? And what should you know before you buy it?

Breaking the Myth...
The plant Cannabis sativa, better known as marijuana, has been used for medical purpose throughout human history. Back in China 5000 years ago, the first record was traced when extracts of the plant were used for relief of cramps and pain. Nowadays, the widely-documented uses of marijuana include anti-nociception, anti-inflammation, anticonvulsant, anti-emetic, as well as recreational use.
Cannabidiol (CBD) is a naturally and a non-psychoactive compound found in the resinous flower of the cannabis plant (representing up to 40% of its extracts). It has generated significant interest among scientists and physicians in recent years, but how CBD exerts its therapeutic impact on a molecular level is still being sorted out. Today the therapeutic properties of CBD are being tested and confirmed by scientists and doctors around the world.
CBD is closely related to another important medicinally active: tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the compound that causes the high that cannabis is famous for. Both CBD and THC have significant therapeutic attributes, but unlike THC, CBD does not make a person feel “high” or intoxicated. That’s because CBD and THC act in different ways on different receptors in the brain and body. The fact that CBD is therapeutically potent as well as non-intoxicating, and easy to take as a CBD oil, makes it an appealing treatment option for those who are cautious about trying cannabis for the first time.
Due to the clinical application of cannabis and the non-psychoactive nature of most phytocannabinoids except THC, the therapeutic potential of this compound has been greatly appreciated. Although this area of research is quite controversial and debatable, several phytocannabinoids, especially cannabidiol (CBD), have been suggested to exert beneficial effects in various pathological conditions, including inflammation, cancer, addiction and epilepsy.
CBD Oil
What exactly is it? Where does it come from? How is it made? And what should you know before you buy it?
CBD oil is extracted from the resinous trichomes of cannabis plants. There are many different cannabis “strains” or varietals. The amount of CBD present in the trichomes will depend on the particular variety of cannabis or hemp. Low resin industrial hemp, which is legally defined as cannabis with less than 0.3 percent THC by dry weight, has fewer trichomes – and therefore less oil – than high-resin cannabis varietals.
But most high resin cannabis strains these days are THC-dominant with little CBD. So choosing the appropriate CBD-rich cannabis chemovar, a variety of cannabis defined by its chemical constituents, is key for extracting CBD oil.


A tiny amount of THC...
According to current federal law, cannabis is considered hemp – not marijuana – as long as no part of the plant (including the leaves and flowers) exceeds a THC concentration of “more than 0.3 percent on a dry weight basis.” Any plant that tops 0.3 percent THC is considered marihuana and is therefore federally illegal to grow, according to law.
Federal law includes a recently added caveat that officially characterizes industrial hemp as having no more than 0.3 percent THC by dry weight. Products containing such a tiny amount of THC should not have an intoxicating effect.
Cannabis is a highly adaptable botanical; it can thrive in various environments, legal and ecological. It responds well to the human hand, which has stretched the genetic capabilities of the plant in unprecedented ways.
Farmers are now growing high resin cannabis (“marihuana”) with less than 0.3 percent THC.
If grown, extracted and processed well, these CBD-rich plants qualify as good starter material for manufacturing CBD oil for medicinal and personal use.
How CBD works?
Believe it or not: our body was made for CBD. All human beings and most animals, have an endocannabinoid system (ECS) with receptors throughout our bodies. The endocannabinoid system (ECS) can be found in almost every part of our body, but especially the nervous system and immune system. A healthy endocannabinoid system means the ECS balances our cells and organs, in a few words: it’s the Yin and Yang of the body.
The endocannabinoid system plays a crucial role in regulating a broad range of physiological processes that affect our everyday experience – our mood, our energy level, our intestinal fortitude, immune activity, blood pressure, bone density, glucose metabolism, how we experience pain, stress, hunger, and more. This system is involved in almost all brain and body functions from our ability to handle pain, stress, and anxiety, sleep disorders… to our mobility and muscle health. In a few words, it keeps our bodies in balance. What are the consequences of a chronically deficient or overactive endocannabinoid system? In a word, disease.
In order to maintain this balance, the endocannabinoid system (ECS) regulates physical and emotional processes like appetite and mood. It does this with substances called endocannabinoids, which are neurotransmitters. Simply put, neurotransmitters are “chemical commands” that one cell releases to tell another cell what to do, creating a specific biological response. CBD from hemp is a natural supplement that keep us all, in optimal health condition!.
Endocannabinoid System

Endocannabinoid System Receptors
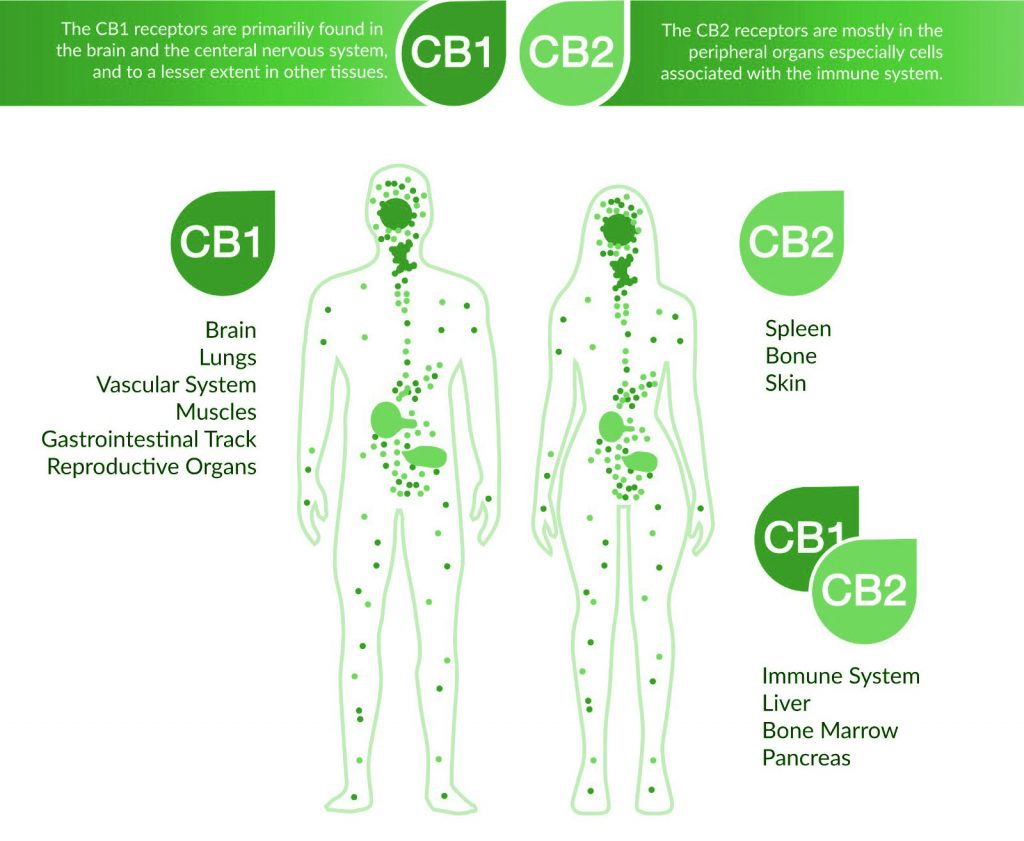
Cannabinoid receptors, located throughout the body, are part of the endocannabinoid system, which is involved in a variety of physiological processes including appetite, pain-sensation, mood, and memory.
Receptors type CB1 are consider to be one of the most wide-range receptors and are present in very high levels in several brain regions. These receptors mediate many of the psychoactive effects of cannabinoids, althougt they can also be found in other parts of the body. The CB1 receptor, is the prominent subtype in the central nervous system and has become one of the best-studied endocannabinoids, due to the greater results shown during potential therapeutic treatments and several pathological conditions, including neuropsychological disorders and neurodegenerative diseases.
Receptors type CB2 have a more restricted distribution, being found in a number of immune cells and in a few neurones. They are mainly involved on the immune system, on macrophages and they are also expressed on peripheral nerveterminals. These receptors play a role in antinociception, or the relief of pain. While the most likely cellular targets and executors of the CB2 receptor-mediated effects of endocannabinoids or synthetic agonists are the immune and immune-derived cells, the number of other potential cellular targets is expanding, now including endothelial and smooth muscle cells, fibroblasts of various origins, cardiomyocytes, and certain neuronal elements of the peripheral or central nervous systems.
CBD and THC have many of the same medical benefits. They can provide relief from several of the same conditions. However, CBD doesn’t cause the euphoric effects that occur with THC. Some people may prefer to use CBD because of the lack of this side effect.
CBD vs. THC

Chemical Structure
Both CBD and THC have the exact same molecular structure: 21 carbon atoms, 30 hydrogen atoms, and 2 oxygen atoms. A slight difference in how the atoms are arranged accounts for the differing effects on your body.
Both CBD and THC are chemically similar to your body’s own endocannabinoids. This allows them to interact with your cannabinoid receptors.
The interaction affects the release of neurotransmitters in your brain. Neurotransmitters are chemicals responsible for relaying messages between cells and have roles in pain, immune function, stress, sleep, to name a few.
Psychoactive Components
Despite their similar chemical structures, CBD and THC don’t have the same psychoactive effects. In fact, CBD is a nonpsychoactive compound. That means it doesn’t produce the “high” associated with THC.
THC binds with the cannabinoid 1 (CB1) receptors in the brain. It produces a high or sense of euphoria.
CBD binds very weakly, if at all, to CB1 receptors. In fact, it can interfere with the bindng of THC and dampen the psychoactive effects.

- CBD is considered “MEDICAL” and THC is considered “RECREATIONAL”.
- CBD is more effective when combining together with THC.
- CBD is not psychoactive (Psych activity is inherently an adverse side effect).
- CBD is fully legal in the United States, because it’s no longer consider a “controlled substance”.
- CBD is sedating and THC causes the “high” that cannabis is famous for.


